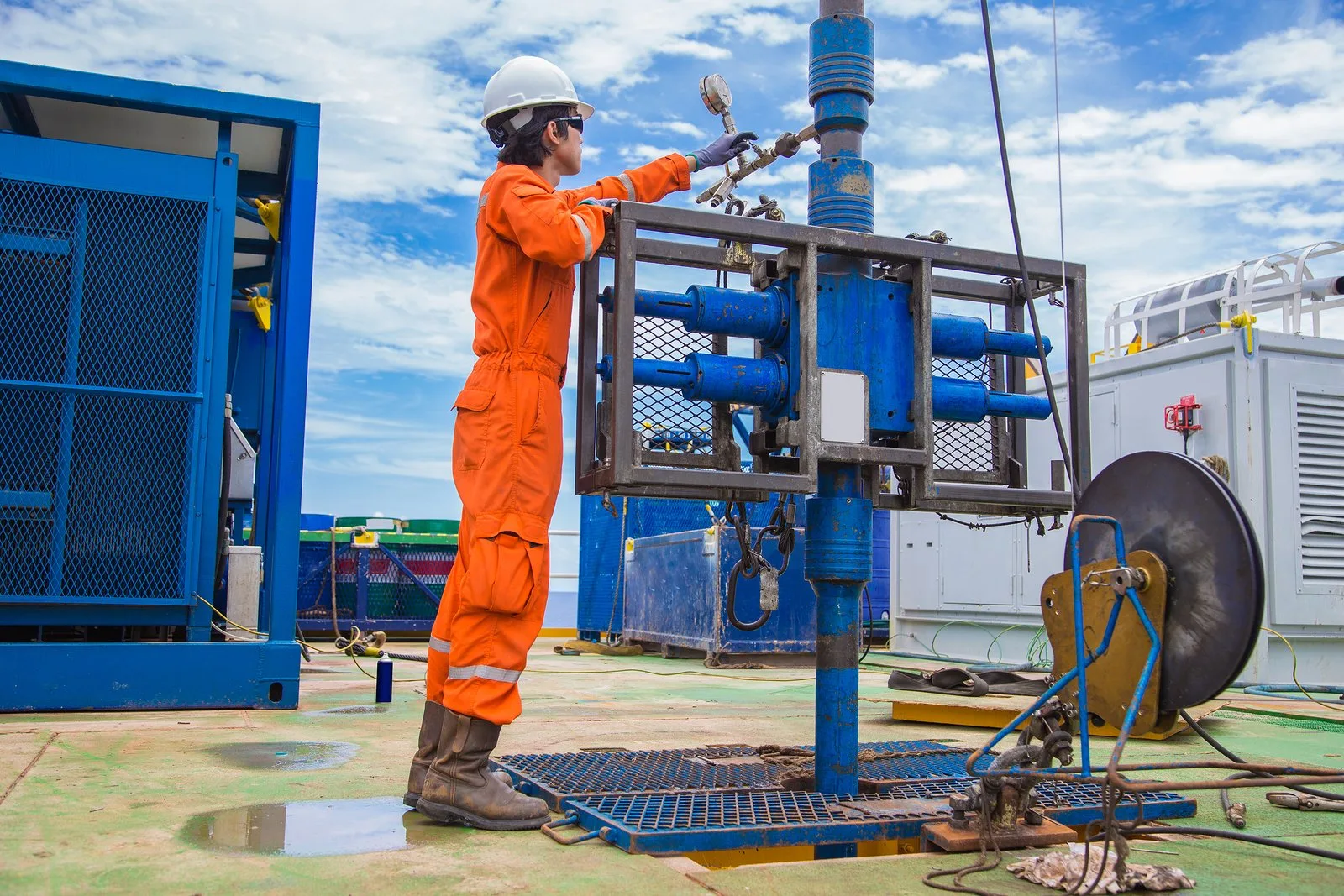
Well completion is the final phase of preparing an oil or gas well for production. It involves various processes and techniques to enable the extraction of hydrocarbons from the reservoir. Activities include casing, cementing, perforation, installing tubing, and using technologies to optimize production and ensure well integrity. The goal is to establish a secure and efficient connection between the reservoir and surface facilities.
Well workover involves maintenance, repair, or enhancement operations on an existing oil or gas well to improve productivity. It addresses issues like declining production, equipment malfunctions, or wellbore damage. Activities include tubing replacement, wellbore repairs, reservoir stimulation, and other measures to optimize performance and extend the well’s life. The goal is to maximize production potential and ensure efficient operations.
What Is Well Completion and Workover Training Course Objective?
PetroSync’s training course emphasizes the practical implementation of diverse techniques and approaches in well completion. After completing the course, you will possess the skills to strategically plan operations by acquiring practical knowledge in designing, planning, and safely installing efficient well completions and workovers. This will result in enhanced well productivity through the integration of completion processes with future production, thereby improving performance and mitigating failures.
What Is Well Completion and Workover Training Course Outlines?
The outline of PetroSync’s Well Completion and Workover training course is listed down below. You can refer to PetroSync’s Well Completion and Workover training course brochure for a more detailed and complete outline.
Day 1 Well Completion and Workover Training
Pre-course test
Module 1: Reservoir Characteristics & Well
- Completion Concept
- Porosity, Permeability, Relative Permeability, and Saturation
- Natural Fracturing and Hydraulic Fracturing
- Pressures, Reservoir Pressure, Basic Pressure calculations, and Pressure Differential
- Well Temperature and Well performance
- Formation Damage: Causes and Prevention of formation damage
- Introduction to well completion (operationally & technically)
- Darcy’s law and skin effect/damage
Module 2: Well Completion Types
- Introduction to Completion Design
- Reservoir completion and Well Completion Classification
- Completion Components (Features & Usage)
- Tubing Performance
- X-mas tree, Wellhead, Casings, Liners
- Production tubing string, Packers
Case Study:
Introduction to full field development
Impact of different well environments on completion design (low porosity, low permeability, H2S, CO2, high GOR, etc.).
Day 2 Well Completion and Workover Training
Quizzes & Recap
Module 3: Reasons for Work-overs and Well Preparation
- Formation damage, Sand control, Acidizing, and Corrosion
- Hydraulic fracturing and Mechanical problems
- Enhancing production through artificial lift methods: Gas lift, ESP, JP, SRP
- Production chemistry: handling challenging reservoir environments (introduction to reservoir fluids, identification of common production problems, mitigation of production problems such as scale, wax, hydrates, asphaltenes, reservoir souring & H2S).
- Well Preparations for workover
- Tree and BOP installation/rigging down
- Change of objectives: Excessive gas & water production
Module 4: Tubing Stresses, Completion Selection, and Operations
- Tubing Stress Analysis and Purpose of Stress Analysis
- Stress loads
- Completion of operations base preparation
- Rig Preparation and completion installation process
Module 5: Overview of Surface & Subsurface Wellbore Equipment & Procedures
- Blowout preventer stacks and components
- Workstring and production tubing
- Auxiliary well control equipment
- Plugs & Packers
- Verification of shut-in
Case Study:
Importance of well completion design and selection on
completion running and future operations.
Tubing stress calculations
Day 3 Well Completion and Workover Training
Quizzes & recap
Module 6: Barriers, Completion, and Work-over Fluids
- Philosophy and Operation of Barrier Systems, Levels of Barriers, Types of Barriers, and Barrier Management
- Influx Detection
Well Control Principles, including:
- Primary Well Control
- Kick Fundamentals
- Tripping practices
- Drilling Fluids
- Secondary well control
- Tertiary well control
- Barrier Definition and Theory
Module 8: Well Control Equipment, including:
- BOP configuration, requirements, and operations
- BOP closing unit function and performance
- Manifolds and pipes
- Valves
- Auxiliary well control equipment
- Accumulator
- Choke and kill manifold
- Circulation system
- Well Killing Operations
Case Study:
Deepwater horizon blowout & well control problem
Day 4 Well Completion and Workover Training
Quizzes & Recap
Module 9: Well Intervention Operations
- Conventional & Non-Conventional:
- Impact of well completion on well intervention operations
- Workover Operations
Module 10: Kick Causes, Warning Signs, Kill Methods, Risk Awareness & Organizing Well Control Operation, Natural Flowing & Artificial Well Workover Programs
- Well shut-in and killing considerations
- Well control problems
- Objective of well control techniques
- Bullheading Volumetric method
- Lube and Bleed
- Forward circulation
- (Driller’s) Method
- Reverse circulation
- Handling kill problems
- Potential impacts of a well control event
- Well integrity
Case Study:
3 case studies by you
Day 5 Well Completion and Workover Training
Module 10: Kick Causes, Warning Signs, Kill Methods, Risk Awareness & Organizing Well Control Operation, Natural Flowing & Artificial Well Workover Programs
- Pressure control equipment/Barrier envelope considerations
- Personnel assignment
- Plan responses to anticipated well-control scenarios
- Blockages & trapped pressure in tubing/wellbore
- Blockage & restricted access in tubing/wellbore
- Hydrates
- H2S considerations
- Natural flowing and artificial well workover programs
Module 11: Emerging Techniques
- Fiber optics: Distributed Temperature System (DTS), Pressure/ temperature (P/T), etc.
- Interventionless packers (Hydrostatic packers, swelling packers, etc.)
- In-situ self-generating weak acid
- Expandable Sand Screens (ESS)
- Sand Control in High angle and long interval: Alternate path technology (SHUTS, CAPS, etc.)
- Formation Isolation Valves (FIV)
- Intelligent & Smart Well Completion: Interval Control Valves (ICV)
- Underbalanced Drilling & Completion
- Cased Hole Circulation Drilling & completion
Who Should Attend a Well Completion and Workover Training Course?
The course is intended for mechanical, maintenance, and inspection/QAQC professionals actively engaged in pressure vessel equipment, although it is not restricted to these specific roles.
- New Drilling Engineers with 0-10 years of experience
- Drilling Engineers with field experience 0-10 years of experience
- Drilling Supervisors with 0-10 years of experience
- Production Engineers with 0-10 years of experience
- Petroleum Engineers with 0-10 years of experience
- Reservoir Engineers with 0-10 years of experience
- Petrophysicist with 0-10 years of experience
- Both Field and Administration Staff of Drilling related service companies with 0-10 years of experience
Enhancing the skills through well completion and workover training course is crucial in the oil and gas industry. These comprehensive programs provide the knowledge and expertise required for successful well intervention performed by petroleum engineers. By enrolling in PetroSync’s Well Completion and Workover training course, you gain practical insights into effective strategies, equipment selection, and optimization techniques for well completion and workover operations.
Well Completion and Workover training course by PetroSync helps you learn to diagnose and address well performance issues, ensuring safe and efficient operations. Enroll today and make a significant impact on your well operations and workover with PetroSync!
Credit Header Image: iStockphoto.com
Reserve Your Training Seat!
Enhance your skills with the latest industry knowledge. Kickstart your career growth with PetroSync training today!

SEO specialist by day, fact-checker by night. An avid reader and content writer dedicated to delivering accurate and engaging articles through research and credible sources.