Oil refining is the process of converting crude oil into a variety of useable products. Crude oil contains hydrocarbons, and industries separate and process it to produce products that fulfill various industrial, commercial, and consumer needs. The oil refining process has multiple steps, including distillation, cracking, reforming, and treatment.
These steps play a critical role in separating crude oil into simpler components, enabling further processing or mixing to generate gasoline, diesel, and other petrochemical products. In the first stage, operators use distillation to separate crude oil into various components based on their boiling points. Over time, engineers implement novel technologies such as cracking to convert heavy fractions into lighter ones.
More valuable compounds this process is critical to the oil and gas industry, which contributes significantly to the world economy. Refining is necessary to meet the demand for goods that fuel vehicles, airplanes, power plants, and other applications.
What Does An Oil Refinery Do?

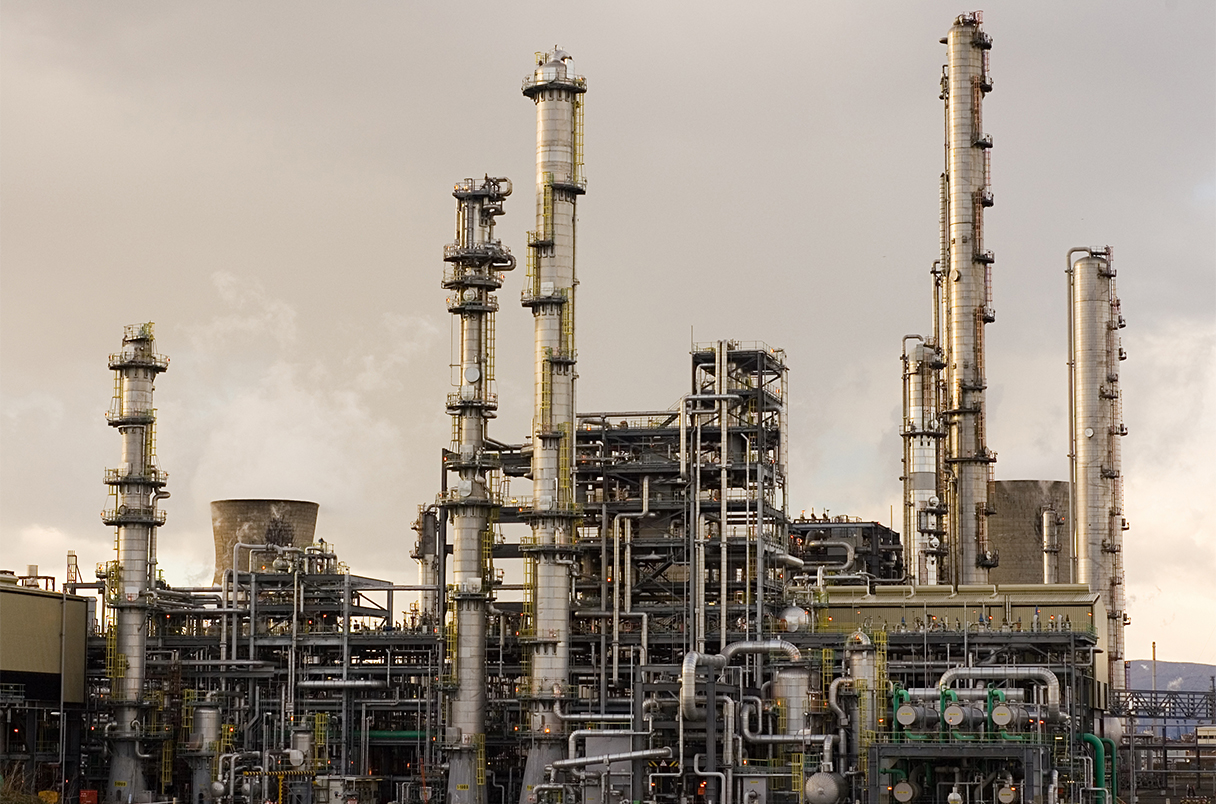
An oil refinery is a complex facility designed to convert (refine) crude oil into a variety of useful products, breaking down the raw crude into different components through a refining process. This intricate process results in the production of essential items such as gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and various petrochemicals.
The refinery plays a crucial role in separating and purifying the crude oil, enabling the creation of a diverse range of products that power our daily lives and contribute to numerous industries. In essence, an oil refinery serves as a vital hub in the energy sector, providing the refined products that drive our modern world.
These refined products serve a multitude of purposes, functioning as fuels for transportation, heating, and electricity generation. Gasoline powers our cars, diesel fuels our trucks, and jet fuel propels airplanes. Beyond transportation, the products derived from oil refineries are integral in heating homes, paving roads, and generating electricity to illuminate our cities.
Moreover, these refined materials serve as essential feedstocks in the chemical industry, contributing to the creation of various chemicals and materials crucial in the manufacturing sector. The intricate processes within an oil refinery, therefore, not only fulfill our energy needs but also play a pivotal role in providing the foundational components for numerous products that shape our modern way of life.
How Does An Oil Refinery Operate?
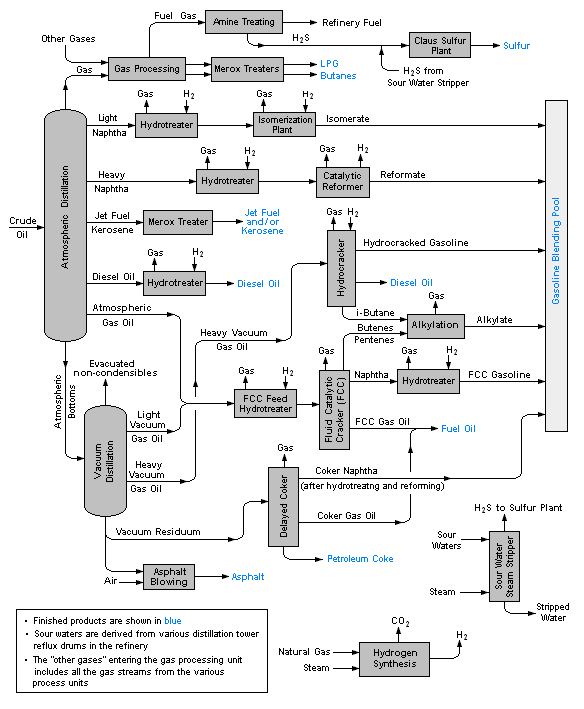
Before we delve into the refinery process, it’s crucial to grasp that oil refineries are highly complex facilities. Their primary role is to turn crude oil into various essential products through a carefully orchestrated sequence of steps.
These steps, ranging from distillation to conversion processes, play vital roles in breaking down crude oil into valuable components. Let’s break down the detailed operation of an oil refinery:
1. Crude Oil Intake
The process begins with the arrival of crude oil at the refinery. Tankers or pipelines transport the crude oil to the facility, where it undergoes initial assessments for quality and composition.
2. Distillation
The first major step is distillation, where the crude oil is heated in a furnace, turning it into vapor. This vapor rises through a distillation column, with different components condensing at various heights. Lighter components like gases and gasoline rise to the top, while heavier components like diesel and residual oil collect at the bottom.
3. Fractionation Towers
The distillation column is essentially a series of fractionation towers. Each tower is designed to capture specific components of the crude oil, creating a range of products. For example, one tower may focus on producing gasoline, while another concentrates on diesel.
4. Conversion Processes
Some components of crude oil need further processing through conversion techniques. Common conversion methods include cracking, where larger hydrocarbons are broken down into smaller, more valuable ones, and reforming, which enhances the quality of gasoline.
5. Treatment and Desulfurization
The refined products undergo treatment to remove impurities and undesirable elements. Desulfurization is a critical step to reduce sulfur content in fuels, addressing environmental concerns and ensuring compliance with regulations.
6. Blending
The refinery blends different refined products to achieve specific qualities and meet market demands. This step is crucial for producing fuels with the desired characteristics, such as octane rating for gasoline.
7. Final Product Storage
The refined products are then stored in tanks before being transported to distribution points. These tanks are often massive structures designed to handle a variety of products safely.
8. By-Product Management
Throughout the refining process, by-products such as petcoke (petroleum coke) and asphalt are generated. Refineries manage these by-products, either utilizing them for other industrial purposes or finding environmentally responsible disposal methods.
9. Environmental Controls
Modern refineries incorporate extensive environmental controls to manage emissions. Advanced technologies, such as catalytic converters and scrubbers, are employed to reduce air pollutants and minimize the environmental impact of refining activities.
10. Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Refineries implement continuous monitoring systems to track the efficiency of operations and product quality. Regular optimization efforts ensure that the refining processes remain efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally responsible.
Which Is The Largest Oil Refinery in The World?
The world’s largest oil refinery is India’s Jamnagar Refinery. With a capacity of around 1.24 million barrels per day, it is the world’s largest single-site refinery. The Jamnagar complex has a huge impact on the global oil market by processing large quantities of crude oil into a variety of high-demand goods.
This refinery is part of the Reliance Industries group and has played an important role in establishing India as one of the world’s leading oil refining countries. Jamnagar’s large capacity is a result of its advanced refining technologies and its strategic location near a major port.
It acts as a petroleum product distribution hub for both Indian and foreign markets. Refining facilities like as Jamnagar contribute to the stability of global oil supplies by assuring the consistent production of refined products that are required by industries globally.
Are Oil Refineries Bad for The Environment?
Oil refineries, while important for producing the fuels that power modern economies, have major environmental consequences. The refinement process may harm the air, water, and soil. Air pollution is caused by refinery emissions that contain hazardous substances such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particle matter.
These pollutants are hazardous to both human health and the environment, resulting in smog, acid rain, and other ecological issues. However, contemporary oil refineries are increasingly taking steps to reduce their environmental impact. New technology and laws demand refineries to use greener processes, lower emissions, and enhance waste management.
Refineries are continually researching ways to integrate renewable energy sources and reduce their carbon footprint. With increasing demand for cleaner energy, the oil and gas industry is changing to satisfy higher environmental criteria while still providing critical services to the global economy.
What Is The Capacity of Indonesia Oil Refinery?
Indonesia’s oil refining capacity has continuously grown, aided by the existence of many large-scale refineries around the country. The Cilacap Refinery, located on Java Island, stands out as Indonesia’s largest. This facility, which can handle roughly 348,000 barrels per day, is recognized as a major refining center in Southeast Asia.
The Cilacap refinery is operated by Pertamina, Indonesia’s state-owned oil and gas business, and it is crucial to satisfying the country’s domestic demand for refined oil products. The Indonesian government has also made major expenditures to increase refining capacity to meet the country’s expanding energy demands.
With ongoing oil and gas training and oil and gas courses, the nation is working towards improving its refinery operations to become more efficient and environmentally sustainable. Expanding refining capacity will also reduce Indonesia’s reliance on oil imports and improve energy security in the long term.
Join PetroSync’s Expert Training for Oil and Gas Professionals
PetroSync provides expert training programs tailored to the needs of professionals in the oil and gas industry. PetroSync provides comprehensive training on many elements of oil refining, petrochemical processing, and environmental management, equipping learners with the information and skills required to succeed.
Our oil and gas training provides real-world insights and practical applications to help you get started or improve your skills. Don’t pass up the opportunity to attend PetroSync’s expert-led training and advance your career.
Credit: Freepik

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.







