In today’s ever-evolving industry landscape, RBI Implementation has emerged as a game-changer, providing most industries like oil and gas, petrochemical, and energy industries with a robust framework for effective risk management and financial stability.
What Is Risk-Based Inspection?
Risk-Based Inspection (RBI) is an optimal maintenance approach utilized to inspect industrial equipment like pressure vessels, doors with quick-opening closures, heat exchangers, and piping. RBI serves as a method for making informed decisions to improve inspection plans.
How To Implement Risk-Based Inspection?
In the field of industrial asset management and safety, Risk-Based Inspection (RBI) is a vital methodology. It serves two key purposes: ensuring equipment reliability and enhancing maintenance efficiency, which leads to cost savings.
Step 1: Data Gathering: The Bedrock of RBI
Data gathering is the foundation of RBI because it provides the essential information needed to assess and manage risks effectively.
1. Acquiring Design and Construction Data
One of the initial steps in implementing RBI involves gathering comprehensive data related to design and construction. This includes information about materials, specifications, and engineering drawings. This data serves as the foundational reference for assessing the integrity of assets.
2. Understanding Process and Operating Data
An in-depth understanding of the operational conditions is major for RBI. This includes data on variables such as pressure, temperature, flow rates, and chemical properties. It makes the understanding of the process aids in evaluating the risks associated with equipment operation important.
3. Examining Inspection and Maintenance History
A thorough examination of inspection and maintenance history provides valuable insights into the health of equipment. It helps in identifying recurring issues and trends, especially in the determination of suitable inspection intervals and strategies.
4. Reviewing Damage Mechanisms
Identifying potential damage mechanisms, their rates, locations, and failure modes is a critical aspect of RBI. This step entails a detailed analysis of factors that could compromise equipment integrity.
Step 2: Risk Assessment: Evaluating Consequences and Probability of Failure
Risk assessment is crucial as it helps identify potential problems by evaluating both the impact of failures and the likelihood of them occurring.
1. Assessing Consequences of Failure (CoF)
Estimating the consequences of a loss of containment is a fundamental aspect of RBI. CoF assessment encompasses the evaluation of the impact on safety, health, the environment, and economics.
2. Determining Probability of Failure (PoF)
PoF assessment involves ascertaining the likelihood of a loss of containment event. It relies on factors such as damage mechanisms, the effectiveness of the inspection program, and historical data.
Step 3: Risk Prioritization: Quantifying and Ranking Risks
Risk prioritization helps determine which issues should be addressed first, ensuring that resources are allocated to the most critical risks.
1. Calculating Risk for Each Specific Consequence
Once CoF and PoF assessments are complete, it becomes possible to quantify the risks associated with each consequence. This step involves numerical calculations to prioritize risks effectively.
2. Conducting Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis is crucial for validating the calculated risks. It ensures that the inputs and assumptions are accurate, providing confidence in the risk assessments.
3. Presenting Risk Findings
Effectively communicating risk findings to stakeholders is vital. Clarity in presenting risks facilitates decision-making and the prioritization of risk mitigation efforts.
4. Establishing Acceptable Risk Levels
Determining acceptable levels of risk is a pivotal step in RBI. It assists in identifying which risks require immediate mitigation measures.
Step 4: Inspection Planning: Crafting a Robust Inspection Strategy
Inspection planning is vital in RBI as it outlines how and when inspections should be conducted, ensuring that they focus on high-risk areas, which helps prevent failures and maintain safety.
1. Identifying Risk Drivers
Understanding the factors contributing to risk is key. This involves pinpointing the root causes of high-risk scenarios and addressing them proactively.
2. Defining Inspection Methods, Scope, and Intervals
Based on risk assessments, an RBI implementation should outline the inspection methods, the extent of inspections, and their intervals. This ensures that inspections are focused on high-risk areas.
3. Exploring Other Risk Mitigation Measures
Apart from inspections, other risk mitigation measures, such as equipment replacement, repair, modification, redesign, or process adjustments, should be considered to reduce risk effectively.
4. Assessing Residual Risk
Determining the level of risk that will remain after executing the mitigation plan is essential. This residual risk informs ongoing risk management strategies.
Step 5: Risk Mitigation: Taking Measures to Reduce Risks
Risk mitigation is integral to RBI as it involves implementing actions to reduce identified risks, ultimately safeguarding assets and preventing potential failures.
1. Implementing Risk-Based Inspection Plans
Executing the defined inspection plans is a critical step. This ensures that inspections are carried out effectively and efficiently, targeting identified high-risk areas.
2. Establishing Integrity Operating Windows (IOWs)
Integrity Operating Windows (IOWs) are operational limits within which equipment must operate to maintain integrity. Defining and adhering to IOWs is fundamental in reducing risk.
3. Addressing Equipment Issues
Depending on the identified risks, equipment may need to undergo replacement, repair, modification, redesign, or rerating to ensure continued safe and reliable operation.
4. Adapting Processes
Process adjustments can significantly impact risk reduction. Changes in operating procedures or materials can mitigate identified risks.
Step 6: Reassessment: The Continuous Improvement Cycle
An RBI implementation is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process of improvement. After inspection and mitigation, reassessment is essential to update risk and inspection plans based on the latest data and mitigation results. This iterative approach ensures the continued integrity of assets.
What Is The Best Practice of RBI Implementation?
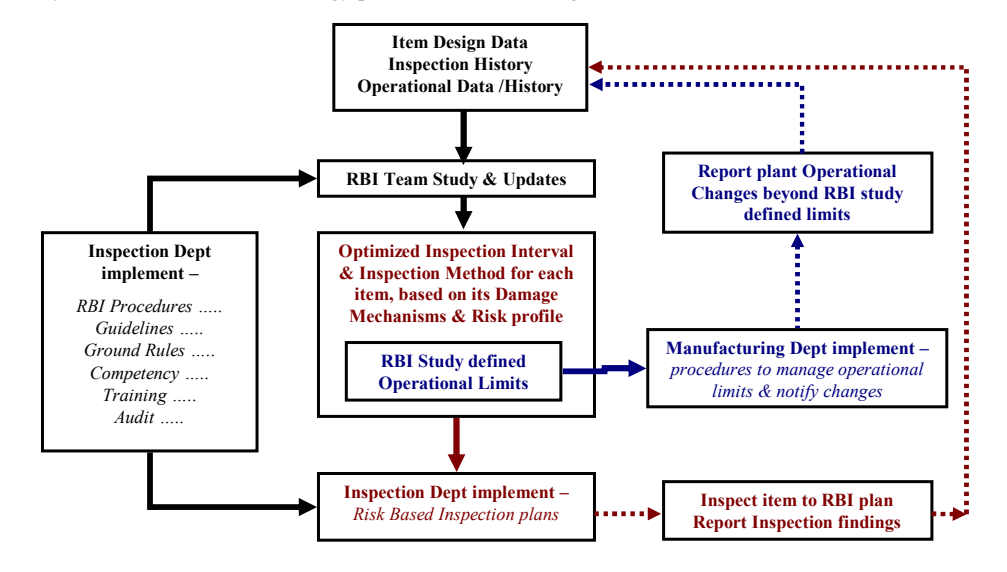
According to Selva and Gordon in What is RBI Best-Practice & How to Implement it Successfully, implementing RBI technology involves gathering data about how the equipment was built, used, and maintained, including any changes over time
A skilled team then assesses the risk to equipment integrity, focusing on identifying potential damage risks. They evaluate the severity of these risks and determine how often inspections should occur. They may also set limits for how the equipment operates and monitor it closely to prevent issues.
To do RBI implementation well, plant operators and chemical engineers must work together and regularly update plans based on inspections and operational changes. This process should become a routine part of the plant’s practices for effective management.
What Are Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of RBI Implementation?
1. What Is The Primary Goal of RBI Implementation?
The primary goal is to enhance safety, optimize maintenance spending, and ensure regulatory compliance by prioritizing inspection efforts based on risk assessment.
2. How Does RBI Implementation Benefit The Oil and Gas Industry?
RBI implementation improves safety, reduces costs, and extends asset life, making it indispensable for the industry.
3. Is RBI Applicable to Other Industries Besides Oil and Gas?
Yes, RBI principles can be applied to various industries, including petrochemicals, manufacturing, and utilities.
4. What Role Does Technology Play in RBI Implementation?
Technology, such as advanced software and data analytics, plays a crucial role in data collection, risk assessment, and monitoring.
5. How Often Should RBI Assessments Be Conducted?
RBI assessments should be conducted regularly to adapt to changing conditions and maintain the integrity of assets.
6. Are There Industry Standards for RBI Implementation?
Yes, organizations can refer to industry-specific standards and guidelines for RBI implementation, ensuring best practices are followed.
In conclusion, a well-executed implementation of Risk-Based Inspection is paramount for industries reliant on critical equipment and safety. By following the structured approach outlined in this guide, organizations can not only meet regulatory requirements but also excel in asset management and risk mitigation, securing their position as leaders in their respective fields.
Implementing RBI is an investment in safety, reliability, and operational efficiency, ensuring a sustainable future for industries. By embracing the principles outlined here, you can not only meet regulatory requirements but also excel in asset management and risk mitigation, securing your position as leader in your respective fields.
Credit header image: Freepik

SEO specialist by day, fact-checker by night. An avid reader and content writer dedicated to delivering accurate and engaging articles through research and credible sources.







