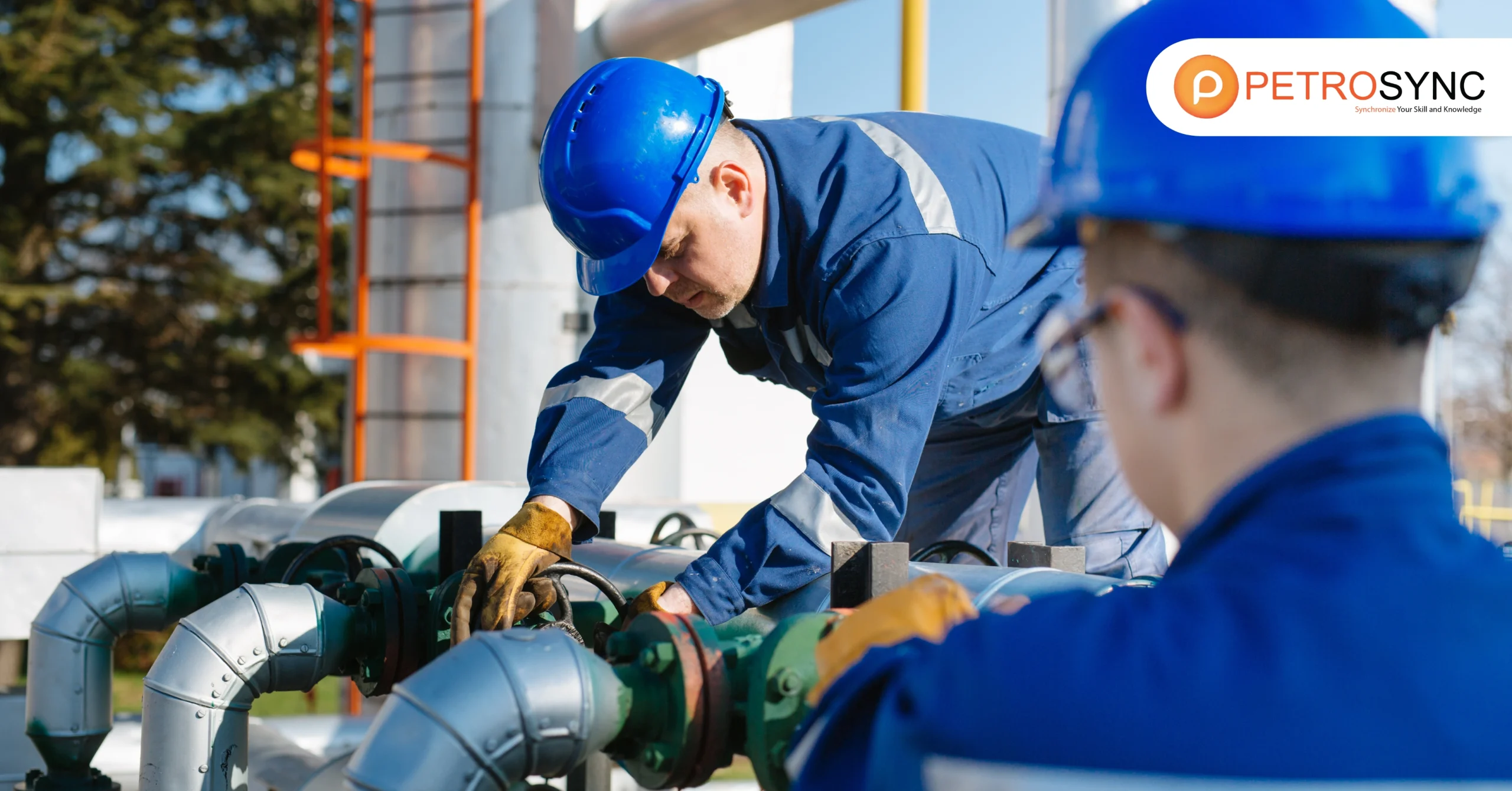
Pressure vessel inspection is a crucial component of overarching asset integrity initiatives. In modern industries, the emphasis on maintenance is highly valued as it serves as a preventive measure against unforeseen accidents. This article explores pressure vessel inspection, addressing its optimal frequency, procedural steps, various methods employed, and a practical checklist.
What Is Pressure Vessel Inspection?
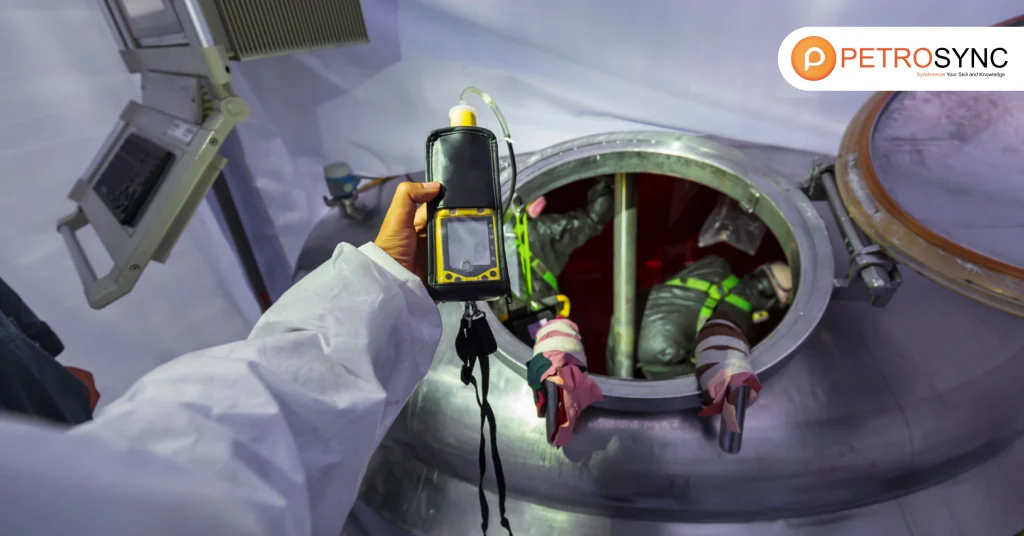
Pressure vessel inspections is involve checking the vessel’s condition from the outside, inside, or both following the guidelines regulated for pressure vessels such as ASME Section VIII and API 510. During these inspections, the pressure vessel inspector must:
- Examine the vessel visually to assess its overall state, including the insulation, welds, joints, and structural connections.
- Measure the thickness to see if the vessel has changed over time due to use.
- Analyze the stress to determine if the vessel is still safe for use.
- Inspect the pressure-release valves to ensure they work correctly.
- Conduct a hydrostatic pressure test to confirm the vessel’s integrity.
How Often Should You Inspect Pressure Vessels?
Pressure vessels play a vital role in several industries, so ensuring they are safe is essential. The frequency of inspections depends on several factors below:
1. Operating Conditions
If a pressure vessel operates under harsh conditions, it requires more frequent inspections. Vessels handling high temperatures or high pressures may need to be checked every few months.
2. Adhering to Regulations
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is crucial. Some regulations dictate how often inspections should occur, so it’s important to stay up to date to avoid penalties and ensure safety as the update covers the most recent findings and inventions.
3. Vessel History
The past maintenance and inspection history of a vessel can influence how often it needs to be inspected. If a vessel has a history of problems, it may require more frequent checks.
4. Risk Assessment
A risk-based approach considers what could happen if the vessel fails. High-risk vessels need more frequent inspections to minimize potential hazards.
What International Standards Regulate Pressure Vessel Inspection?
1. ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC)
Widely recognized in North America and many other parts of the world, this code sets the standards for the design, construction, and inspection of pressure vessels.
2. API 510
The American Petroleum Institute’s standard specifically addresses the inspection, repair, alteration, and rerating of pressure vessels used in the petrochemical and refining industries.
3. BS EN 13445
This European standard governs the design and construction of pressure vessels. It also outlines the requirements for inspection, testing, and documentation.
How Is The Procedure of Pressure Vessel Inspection Done?
Inspecting a pressure vessel involves a methodical process to find defects and guarantee safe operation. The general process typically includes these steps:
1. Visual Inspection
This step involves a careful visual examination of the vessel’s outer surface and welds to spot visible defects like corrosion or cracks.
2. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
NDT methods like ultrasonic testing and radiography allow inspectors to assess the vessel’s internal structure without causing damage.
3. Measuring Thickness
Measuring the vessel’s thickness helps identify thinning due to corrosion or erosion.
4. Pressure Tests
Hydrostatic testing or pneumatic testing determine whether the vessel maintains its integrity under pressure conditions.
5. Keeping Records
Maintaining detailed records of inspections, findings, and any repairs or modifications is essential.
What Are Some Types of Pressure Vessel Testing?
Pressure vessels require various testing methods to ensure their safety and reliability. Here are the most common methods:
1. Ultrasonic Testing
This technique uses high-frequency sound waves to locate internal defects like cracks or inclusions.
2. Radiographic Testing
X-ray or gamma-ray techniques are used to examine the internal structure and welds for defects.
3. Magnetic Particle Testing
This method involves applying a magnetic field and using iron particles to spot surface and near-surface defects.
4. Liquid Penetrant Testing
A liquid penetrant is applied to the surface, and after a certain period, it is checked for any signs of defects.
5. Visual Testing
Visual testing is the simplest method and involves a thorough visual examination of the vessel’s outer surface and welds.
What Are The Pressure Vessel Inspection Checklists?
A thorough inspection checklist is necessary to ensure everything is noticed during an inspection. Here are several checklist that covers the key aspects of the inspection:
1. General Inspection
This inspection involves a thorough assessment of the pressure vessel, both inside and outside, to ensure it is operating safely and in compliance with regulations. It aims to identify any potential issues that could affect its integrity
| Checklist Items | Descriptions | |
| Visual Inspection | Examine outer surfaces and welds for defects | |
| NDT Reports | Review non-destructive testing reports | |
| Thickness Measurements | Ensure thickness measurements are within acceptable limits. | |
| Pressure Tests | Confirm the results of pressure tests. | |
| Corrosion Assessment | Evaluate corrosion levels and plan for maintenance. | |
| Regulatory Compliance | Verify compliance with relevant regulations. | |
| Documentation Review | Scrutinize inspection records and maintenance history. | |
| Emergency Response Preparation | Prepare for emergencies and possible failure scenarios. | |
2. External Inspection
This inspection concentrates on the visible aspects of the pressure vessel, including its external surfaces, welds, and support structures. It aims to identify any visible defects, such as cracks, corrosion, or signs of wear and tear, which could impact the vessel’s structural integrity and safety.
| Checklist Items | Descriptions | |
| External coverings | inspected for defects (including insulation and corrosion-resistant coatings should be monitored) | |
| Entire vessel exterior | inspected for any kind of leakage of gas, vapor, or liquid | |
| Mountings | inspected to see if they allow for appropriate expansion and contraction | |
| Vessel and vessel connections | inspected for deformations, cuts, cracks, or gouges, including on nozzles, manholes, and reinforcing plates | |
| Nuts, bolts, flange faces, vessel surface | inspected for corrosion or other defects) | |
| Shell surfaces and heads | inspected for blisters, bulges, or other deformations | |
| Welded joints and adjacent areas | inspected for cracks or defects | |
3. Internal Inspection
This inspection focuses on a detailed examination of the pressure vessel’s internal components, surfaces, and structural integrity. Its purpose is to detect defects, corrosion, or damage within the vessel that may compromise its performance or safety.
| Checklist Items | Descriptions | |
| Interior of vessel | inspected for cracks, blistering, corrosion, deformation, or any other defects | |
| Threads | inspected to ensure the adequate number of threads are engaged on threaded connections | |
| Openings | leading to any external fittings or controls inspected to ensure they are free from obstruction | |
| Special closures | inspected to ensure they are adequate | |
| Areas of high stress concentration | inspected for cracks or other wear | |
What Are Some FAQs Regarding API 510 Inspection?
1. What are the consequences of neglecting pressure vessel inspections?
Neglecting inspections can lead to severe failures, resulting in injuries, environmental harm, and financial losses. Regular inspections are crucial to prevent these risks.
2. How can I ensure compliance with inspection regulations?
Stay updated with industry regulations and standards and work with certified inspectors who can guide you to compliance.
3. Are there non-intrusive methods for pressure vessel inspection?
Yes, non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as ultrasonic and radiographic testing, allow inspection without causing harm.
4. How frequently should I inspect my pressure vessel?
The inspection frequency depends on operating conditions, regulations, vessel history, and risk assessment. It can range from monthly to every few years.
5. What should I do if an inspection reveals defects in my pressure vessel?
If defects are found, consult with a qualified inspector to determine the seriousness and necessary actions, which may involve repairs, replacements, or modifications.
6. Can I perform pressure vessel inspections myself?
Inspecting pressure vessels requires specialized knowledge and equipment. It’s advisable to hire certified API 510 inspectors for accurate and safe assessments.
In conclusion, pressure vessel inspection is like giving a thorough checkup to a crucial piece of equipment. We have international rules and guides, such as the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, API 510, and BS EN 13445, to ensure that these vessels are safe and sound. These inspections look at the inside and outside, making sure everything is in good condition and that they follow the rules.
By following these guidelines and conducting regular inspections, we can be confident that pressure vessels in various industries are safe, reliable, and ready to do their important jobs. It’s all about keeping everyone and everything safe and sound.
Join PetroSync’s Pressure Vessel Inspection Training Today!
When it comes to learning how to perform pressure vessel inspections, PetroSync has you covered. We offer API 510 training program that equips you with the essential knowledge and skills needed for this critical task. This API 510 training is designed to help you become proficient in running a pressure vessel inspection.
With PetroSYnc’s guidance, you can contribute to the safety and efficiency of various industries by ensuring pressure vessels are in good shape and ready for their duties.

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.







