Embarking into the world of industrial boilers, ASME Section I emerges as a crucial guide, defining the standards that govern power boilers’ design, construction, and operation. It serves as the cornerstone, aligning precision engineering with stringent safety protocols. Read on to explore the significance of ASME Section I in ensuring the reliability, safety, and efficiency of power boilers across diverse industrial applications.
What Is ASME Section I?
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) was founded in 1880. Its mission is to promote the art, science, and practice of interdisciplinary engineering and allied fields around the globe. ASME has developed numerous codes and standards to ensure the safety and dependability of engineering disciplines, particularly mechanical engineering.
ASME specifies criteria for designing, manufacturing, and inspecting pressure vessels and boilers. High-pressure and temperature systems play a crucial role in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, and energy, emphasizing safety as the top priority.
The ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) is among the most important standards. It oversees the design, construction, and inspection of boilers and pressure vessels to guarantee that they can withstand high pressures without failure. The BPVC is divided into sections, with Sections I and VIII being the most commonly discussed.
What Is The Scope of ASME Section I?
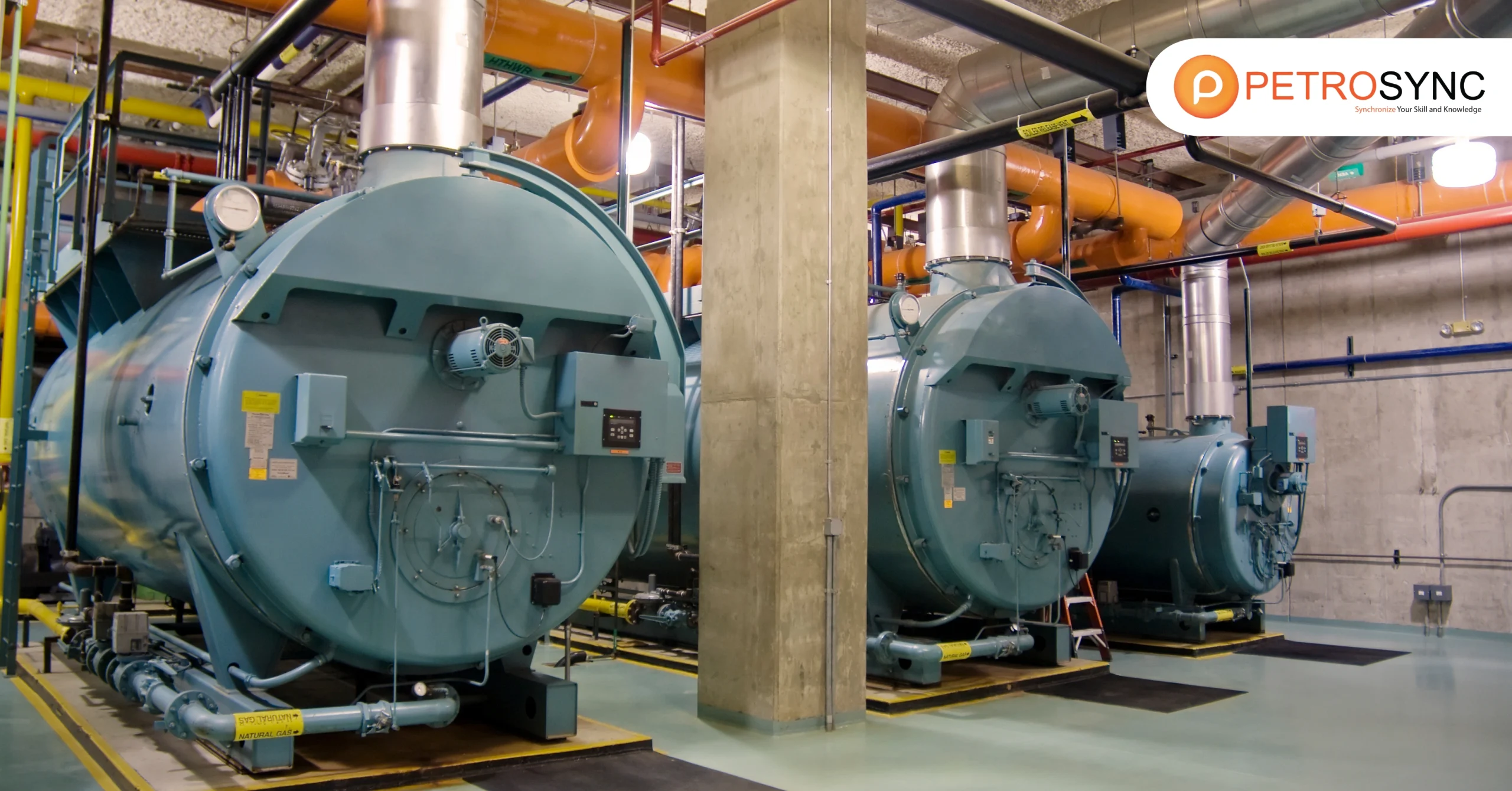
The scope of ASME Section I is broad and encompasses rules and general requirements for the construction of power boilers, electric boilers, miniature boilers, and high-temperature water boilers. These guidelines are applicable to various methods of constructing boilers used in stationary service
|
Boiler Type |
Brief Explanation |
| Boilers | General term referring to devices that generate steam or hot water for various applications. |
| Electric Boilers | Boilers that use electricity as the primary source of energy for heating water or producing steam. |
| Miniature Boilers | Small-scale boilers designed for limited applications, often used in model engines or educational settings. |
| High-Temperature Water Boilers | Boilers specifically designed to produce hot water at temperatures higher than conventional boilers. |
| Heat Recovery Steam Generators | Devices that recover and utilize waste heat to produce steam for additional power generation. |
| Certain Fired Pressure Vessels | Pressure vessels designed to contain and control the release of fluids or gases under pressure, often involving combustion. |
| Organic Fluid Vaporizers | Devices used to convert organic fluids into vapor, typically for industrial processes or heat transfer applications. |
Power Boilers Used in Locomotive, Portable, and Traction Services
ASME Section I ensures that these boilers meet stringent standards for safety, efficiency, and reliability in diverse industrial applications, making it a comprehensive and trusted framework in the field of mechanical engineering.
|
Point |
Explanation |
| Boilers that generate steam or other vapor at a pressure greater than 15 psig | ASME I applies to boilers that produce steam or vapor under pressure exceeding 15 pounds per square inch gauge (psig). These rules ensure their safe and efficient operation. |
| High-temperature water boilers that operate at pressures greater than 160 psig and/or temperatures greater than 250 F | ASME Section I covers high-temperature water boilers operating at pressures exceeding 160 psig or temperatures exceeding 250 degrees Fahrenheit, ensuring their adherence to safety standards. |
| Power boilers used in locomotive, portable, and traction service | The rules extend to power boilers employed in locomotives, portable setups, and traction services, ensuring their design and operation meet ASME standards for safety and reliability. |
| High-temperature water boilers used in stationary service | ASME Section I also applies to high-temperature water boilers used in stationary service, guaranteeing their compliance with safety and operational requirements for stationary applications. |
Additionally, the ASME Certification Mark signifies that stamped items meet the criteria outlined in the most recent edition of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code.
What Is the Difference Between ASME Section I and Section VIII?
ASME Sections I and VIII are both part of the BPVC, but they address different types of equipment and serve different objectives.
1. ASME Section I: Power Boilers
ASME Section I, titled ‘Rules for Construction of Power Boilers,’ specifically outlines the requirements for power boilers, which engineers typically use to generate steam for power production. This section provides guidelines for:
- Design and Construction: It includes rules for the materials, design, fabrication, and inspection of power boilers and high-pressure, high-temperature water boilers. These boilers are widely used in power stations, refineries, and chemical industries.
- Safety Features: Section I outlines specific safety considerations, such as making sure boilers have safety valves to avoid overpressure, as well as thorough criteria for testing and maintaining these safety systems.
- Operational Standards: The document also outlines the operating processes to follow during the installation, use, and inspection of power boilers.
2. ASME Section VIII: Pressure Vessels
ASME Section VIII, “Rules for Construction of Pressure Vessels,” discusses pressure vessels, which are used to store and transfer gases or liquids under pressure :
- Division 1: Provides general requirements for most pressure vessels.
- Division 2: Covers vessels that require higher safety margins and operate under higher stress conditions.
- Division 3: Deals with pressure vessels designed for very high pressures.
The primary distinctions between Sections I and VIII include:
- Application: Section I applies to power boilers, while Section VIII applies to pressure vessels. Boilers generate steam, whereas pressure vessels hold high-pressure gases or liquids.
- Design Pressure and Temperature: Section I focuses on high-pressure, high-temperature equipment, common in power plants, while Section VIII covers a broader pressure range.
- Construction Standards: Section I emphasizes safety by specifically requiring equipment such as safety valves and testing designed for the dynamic situations found in power boilers. Section VIII covers a broader range of sectors that use pressure vessels.
What Are Some Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about ASME Section I?
1. What makes ASME Section I Power Boilers different from other boiler types?
ASME I Power Boilers adhere to strict safety and efficiency standards, setting them apart as an industry gold standard.
2. Are ASME Section I Power Boilers suitable for small-scale applications?
Large settings commonly use these boilers, but they can adapt to smaller applications without compromising safety and efficiency.
3. How often should you conduct maintenance on ASME Section I Power Boilers?
Regular maintenance is essential to uphold safety standards and optimize performance, ensuring longevity and reliability.
4. Can ASME Section I Power Boilers contribute to sustainability goals?
Yes, their efficiency leads to reduced fuel consumption and emissions, aligning with sustainability objectives.
5. What role do smart controls play in ASME Section I Power Boilers?
Smart controls optimize fuel usage and performance, contributing to cost savings and environmental sustainability.
6. How do ASME Section I Power Boilers adapt to varying operational demands?
Their versatility allows seamless adaptation to fluctuating operational demands, ensuring optimal performance in dynamic industrial environments.
In conclusion, ASME I plays a vital role in the industrial landscape as the standard for power boilers. This standard ensures boiler design, construction, and operation meet safety, performance, and reliability criteria effectively.
Join PetroSync’s ASME Section I Training for Enhanced Expertise!
PetroSync, recognizing the crucial importance of understanding the ASME I standard and its broad applicability across industries, has developed specialized training programs. The creators meticulously crafted this program to help you master the intricacies of ASME Section I Power Boilers course. Join this course to gain insights into power boiler design, construction, and operation, ensuring comprehensive preparation.

Results-oriented and thorough SEO specialist with extensive experience in conducting keyword research, developing and implementing digital website promotion strategies and plans, managing campaigns to develop company websites in the digital world, excellent knowledge of marketing techniques and principles, and attentive strong attention to detail.







